How Does Electric Stimulation Therapy Work? Understanding the Power of Electrical Muscle Stimulation

Electric Stimulation Therapy, also known as Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) or Electrical Nerve Stimulation (ENS), is a therapeutic technique that uses electrical currents to stimulate nerves and muscles. This non-invasive treatment has gained popularity in various fields, including physical therapy, rehabilitation, pain management, and even mental health disorders. In this comprehensive article, we will explore how electric stimulation therapy works, its various applications, and its potential benefits.
Understanding the Basics of Electric Stimulation Therapy
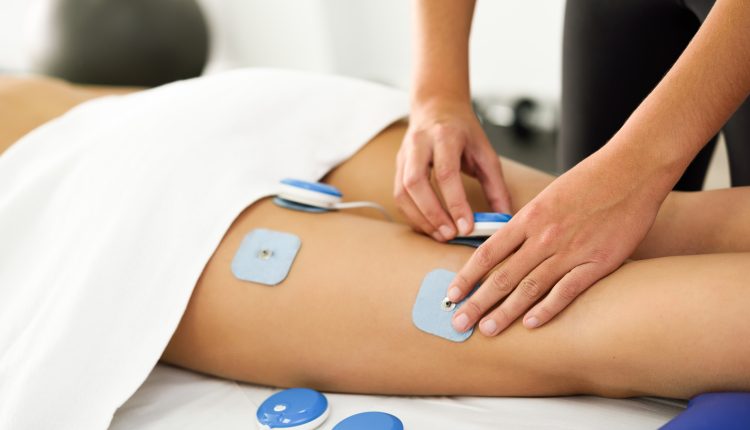
Electric Stimulation Therapy involves the use of specialized devices that deliver controlled electrical impulses to specific areas of the body. These impulses mimic the electrical signals naturally produced by the nervous system. The therapy can be administered through electrodes placed on the skin or implanted devices, depending on the treatment’s requirements.
How Electric Stimulation Therapy Works
When electrical currents are applied to nerves or muscles, they trigger involuntary contractions and stimulate the target area. The process can vary depending on the specific type of stimulation used, but the general mechanisms include:
1. Muscle Stimulation:
Electric stimulation directly activates motor nerves, causing muscles to contract. This is known as Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES). NMES is often used in physical therapy and rehabilitation to prevent muscle atrophy, increase muscle strength, and improve overall muscle function, especially in patients with limited mobility due to injuries or neurological conditions.
2. Pain Relief:
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) is a popular form of electric stimulation therapy used for pain management. TENS units deliver low-frequency electrical impulses that interfere with pain signals traveling to the brain, effectively reducing the perception of pain. It is commonly used to alleviate chronic pain conditions, such as back pain, arthritis, and nerve-related pain.
3. Stroke Rehabilitation:
Electric stimulation therapy has shown promising results in stroke patients during the recovery process. It helps promote neuroplasticity, encouraging the brain to rewire itself and regain lost functions. In stroke rehabilitation, the therapy can target specific muscles affected by hemiplegia, helping patients regain strength and movement.
4. Brain Stimulation Therapies:
Electrical Brain Stimulation therapies, such as Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) and Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS), are used to treat mental disorders like depression and anxiety. These therapies involve stimulating specific areas of the brain to modulate brain activity and improve mood and cognitive function.
The Application of Electric Stimulation Therapy
Electric stimulation therapy is applied through various devices and techniques, each serving specific purposes:
1. TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation):
TENS units are portable devices that can be used by patients at home. They typically have adjustable parameters, such as pulse frequency and intensity, allowing users to customize the treatment for their pain relief needs.
2. NMES (Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation):
NMES devices are commonly used by physical therapists in clinical settings. These devices are designed to target specific muscles and motor nerves to facilitate muscle contractions and improve muscle function.
3. Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES):
FES devices use electric stimulation to activate muscles in paralyzed or weakened limbs, enabling patients to perform functional movements like walking or grasping objects.
4. rTMS (Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation):
rTMS devices use magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain. It has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of certain mental health disorders.
Potential Benefits and Considerations
Electric stimulation therapy offers several potential benefits, including:
- Pain relief without the use of drugs or medications.
- Improved muscle strength and function in rehabilitation settings.
- Enhanced stroke recovery through neuroplasticity.
- Treatment of mental health disorders like depression and anxiety.
However, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
1. Side Effects:
While generally safe, some individuals may experience skin irritation or discomfort at the electrode sites. Following proper guidelines and using appropriate electrode placement can minimize these risks.
2. Individual Variability:
Not everyone may respond equally to electric stimulation therapy. The effectiveness of the treatment can vary depending on the individual’s condition, overall health, and responsiveness to the therapy.
3. Professional Guidance:
To ensure safe and effective application, it is crucial to work with qualified healthcare providers, physical therapists, or professionals experienced in administering electric stimulation therapy.
Research and Clinical Trials
Electric stimulation therapy has been the subject of numerous studies and systematic reviews, evaluating its efficacy and safety across various medical applications. The research continues to evolve, further enhancing our understanding of the therapy’s potential and optimal treatment protocols.
Conclusion
Electric stimulation therapy, encompassing electrical muscle stimulation and electrical nerve stimulation, has become a valuable tool in the fields of physical therapy, rehabilitation, pain management, and mental health treatment. By precisely targeting nerves and muscles with controlled electrical impulses, this non-invasive therapy offers potential benefits in pain relief, muscle strengthening, stroke recovery, and mental health disorders. While further research and clinical trials continue to shed light on its full potential, electric stimulation therapy has proven to be a promising and versatile treatment option for patients seeking alternative and effective healthcare solutions.

Comments are closed.